
Terminology
A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P S T U V W Z
AFUE:Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. A measurement of a gas furnace efficiency in converting fuel to energy – the higher the rating, the more efficient the unit.
AGA: Abbreviation for American Gas Association, Inc.
Air Conditioner: A device that can change the temperature, humidity, orgeneral quality of the air.
Air Cleaner: A device that removes undesirable particles from moving air.
Air Flow Volume: The amount of air the system circulates through your home, expressed in cubic feet per minute (cfm).
Air Handler: An air moving and/or mixing unit.
ARI: Air Conditioning & Refrigeration Institute.
ASHRAE: American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air conditioning engineers.
BTU:British thermal unit; the amount of heat required to raise or lower the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit.
BTUh: British thermal units per hour. 12,000 BTUh equals one-ton of cooling.
Burner: A device that uses fuel to support combustion.
Burner Orifice: The opening through which gas flows to the air/gas mixing chamber of the burner.
Burner (Sealed Combustion): A burner that obtains all air for combustion from outside the heated space.
Capacity:The output or producing ability of cooling or heating systems.Cooling and heating capacities are referred to in British thermal units (BTUs) per hour.
Celsius: The metric temperature scale in which water freezes at zero degrees and boils at 100 degrees, designated by the symbol “C”.
CFM: Abbreviation for cubic feet per minute.
Charge: To add refrigerant to a system.
Compressor: Mechanical device to compress refrigerant gas.
Condensate: Water vapor that liquifies due to the lowering of its temperature to the saturation point.
Condenser Coil (or Outdoor Coil): In an air conditioner, a finned coil which dissipates heat from the refrigerant, changing the refrigerant from vapor to liquid. In a heat pump system, the coil absorbs heat from the outdoors in the
heating cycle.
Condenser Fan: The fan that circulates air over the air-cooled condenser.
Contactor: A switch that can repeatedly cycle, making and breaking an electrical connection.
Crankcase Heater: An electrical resistance heater installed on compressor crankcase.
Damper:A movable plate installed inside ductwork to control airflow.
Defrost: To melt frost.
Degree-day: A degree-day is equal to 65 degrees Fahrenheit minus the mean outdoor temperature.
Dehumidifier: An air cooler that removes moisture from the air.
Diffuser: A grille over an air supply duct having vanes to distribute the discharging air in a specific pattern or direction.
DOE: Department of Energy.
Downflow Furnace: A furnace that intakes air at its top and discharges air at its bottom.
Drain Pan: Also referred to as a condensate pan. This is a pan used to catch and collect condensate (in residential systems vapor is liquefied on the indoor coil, collected in the drain pan and removed through a drain line).
Dry Bulb Temperature: Heat intensity, measured by a dry bulb thermometer.
Dry Bulb Thermometer: An instrument that measures air temperature independently of humidity.
Ductwork: A pipe or conduit through which air is delivered. Ducts are typically made of metal, fiberboard, or a flexible material.
DX: Direct expansion; a system in which heat is transferred by the direct expansion of refrigerant.
EER:Energy Efficiency Ratio (steady state)
Energy StarŪ: The U.S. Department of Energy, Environmental ProtectionAgency (EPA), Energy Star labeled products are more energy efficient and help reduce our whole earth’s pollution problems.
EPA: Environmental Protection Agency.
Expansion Valve: A refrigerant-metering value with a pressure or temperature controlled orifice.
Evaporator Coil (or Indoor Coil): Located inside your home in the indoor unit. This is a finned coil in which a volatile liquid evaporates and absorbs heat. This is where the refrigerant evaporates as it absorbs heat from the indoor air that passes over the coil.
Fahrenheit:The temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees; designated by the letter F.
Fan: A device that creates air currents.
Filter: A device that removes impurities through a straining process.
Flue: Any vent or passageway that carries the products of combustion from a furnace.
Furnace: That part of the heating system in which the combustion of fossil fuel and transfer of heat occurs.
Fuse: A metal strip in an electrical circuit that melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows through it.
GAMA:Gas Appliance Manufacturers Association.
Gas Furnace Heat Exchanger: Located in the furnace, the heat exchanger transfers heat to the surrounding air, which is then pumped throughout your home.
H
Heat Exchanger:An area, box, or coil where heat flows from the warmer to the colder fluid or surface.
Heat Gain: Heat added to the conditioned space by infiltration, solar radiation, occupant respiration, and lighting.
Heating Coil: Any coil that serves as a heat source.
Heat Loss: The rate of heat transfer from a heated space to the outdoors.
Heat Pump: A mechanical-compression cycle refrigeration system that can be reversed to either heat or cool the controlled space.
Heat Transfer: The movement of heat energy from one point to another. The means for such movement are conduction, convection, and radiation.
Hertz: In alternating current (AC electricity), the number of cycles per second.
HSPF: Heating Seasonal Performance Factor. This rating is used in measuring the heating efficiency of a heat pump. The higher the number the more efficient the heat pump system.
Humidifier: A machine that adds water vapor to the air to increase humidity.
Humidistat: A humidity-sensing control that cycles the humidifier on and off.
Humidity: The presence of water vapor in the air.
HVAC: Abbreviation for Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning.
Ignition:The lighting of a fuel to make it burn.
Kilowatt (kW):1,000 watts.
Latent Heat:A type of heat, which when added to or taken from a substance, does not change the temperature of the substance. Instead, the heat energy enables the substance to change its state.
Media:The material in a filter that traps and holds the impurities.
MERV: Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value. An expression of the filtering efficiency of an air filter that has been evaluated using the ASHRAE Standard 52.2 test procedure. MERV values range from less than 1 for disposable panel residential filters to as high as 20 for HEPA filters used in Clean Rooms.
NEC:National Energy Council / National Electric Code.
NEMA: National Electrical Manufacturing Association.
OEM:Original equipment manufacturer.
Orifice: An opening or hole; an inlet or outlet.
Package Unit:A heating and cooling system contained in one outdoor unit. A package unit is typically installed beside, on the roof, or sometimes in the attic of a home.
PSI: Pounds per square inch.
PSIA: Pounds per square inch, absolute.
PSIG: Pounds per square inch gauge.:
PVC: Polyvinyl chloride; a type of plastic.
Reciprocating Compressor:A compressor whose piston or pistons move back and forth in the cylinders.
Refrigerant: A chemical that produces a refrigerating effect while expanding and vaporizing. Most residential air conditioning systems contain R-22 refrigerant. R-22 is regulated under the Montreal Protocol and in the United States by the Environmental Protection Agency. R-22 is scheduled to be in production until the year 2020. It’s used in approximately 95 percent of air conditioning equipment manufactured in the U.S. today.
Refrigerant Charge: The required amount of refrigerant in a system.
SEER:Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio; a measure of cooling efficiency for air conditioners and heat pumps. The higher the SEER, the more energy efficient the unit. SEER is the ratio of the BTU cooling in normal annual use to the total amount of electrical power (watts) over the same period.
Self-Contained System: A refrigerating system that can be moved without disconnecting any refrigerant lines; also known as a package unit.
Sensible Heat. That heat which, when added to or taken away from a substance, causes a rise or fall in temperature.
Sensor: Any device that reacts to a change in the conditions being measured, permitting the condition to be controlled.
Setpoint: The temperature or pressure at which a controller is set with the expectation that this will be a normal value depending on the range of the controller.
Split System: The combination of an outdoor unit (air conditioner or heat pump) with an indoor unit (furnace or air handler). Split systems must be matched for optimum efficiency.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve:A refrigerant metering device that maintains a constant evaporator temperature by monitoring suction vapor superheat; also called a thermal expansion valve.
Thermostat: A thermostat consists of a series of sensors and relays that monitor and control the functions of a heating and cooling system.
Ton: A unit of measurement used for determining cooling capacity. One ton is the equivalent of 12,000 BTUs per hour.
Two-Stage Heating / Two-Stage Cooling: Two-stage heating and cooling is considered to be more efficient because it operates at a lost speed most of the time. However, on days when more heating or air conditioning is required, it switches to the next stage for maximum comfort.
U-Factor:The factor representing resistance to heat flow of various building materials.
UL: Underwriters Laboratories.
Upflow Furnace: A furnace in which air is drawn in through the sides or bottom and discharged out the top.
Vacuum:A pressure below atmospheric pressure. A perfect vacuum is 30 inches Mercury (periodic symbol “Hg”).
Variable-Speed Motor(s): A motor whose speed may be varied.
Volt: The unit of measure used to describe a difference in electrical potential; abbreviated by the symbol “v”.
Voltage: The force that pushes an electrical current along wires and cables.
Watt:The unit of electrical power equal to the flow of one amp at a potential difference of one volt.
Wet Bulb Thermometer: A thermometer whose bulb is covered with a piece of water-soaked cloth. The lowering of temperature that results from the evaporation of water around the bulb indicates the air’s relative humidity.
Zoning System:A method of dividing a space into different comfort zones so each zone can be independently controlled depending on use and need; an air conditioning system capable of maintaining varying conditions for various rooms or zones.
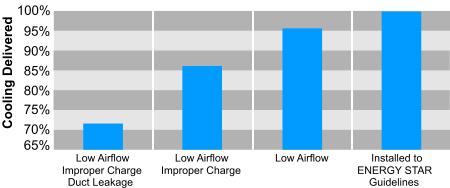
Looking for an affordable way to budget your residential heating and cooling needs? Check out our Priority Service Agreements for details of a plan that provides a means of “Budgeting Your Comfort”.
Alliance Comfort Systems understands the factors that contribute to energy costs. We welcome the opportunity to help reduce your energy costs.
Proudly Serving:
Avondale – Cave Creek – Deer Valley – ElMirage – Fountain Hills – Gilbert – Glendale – Guadalupe
Laveen – Litchfield Mesa – Paradise Valley – Peoria – Phoenix – Scottsdale
Sun City – Sun City West – Surprise – Tempe

